|
| 1 | +--- |
| 2 | +Title: 'step()' |
| 3 | +Description: 'Draws step plots where y-values change at discrete x-positions.' |
| 4 | +Subjects: |
| 5 | + - 'Data Science' |
| 6 | + - 'Data Visualization' |
| 7 | +Tags: |
| 8 | + - 'Graphs' |
| 9 | + - 'Libraries' |
| 10 | + - 'Matplotlib' |
| 11 | + - 'Methods' |
| 12 | +CatalogContent: |
| 13 | + - 'learn-python-3' |
| 14 | + - 'paths/data-science' |
| 15 | +--- |
| 16 | + |
| 17 | +**`step()`** creates a piecewise-constant (step) plot from 1-D data. Each sample in `y` is represented as a horizontal segment and adjacent samples are connected by vertical lines. The `where` parameter controls whether the step change happens before, after, or at the midpoint of the x-coordinate. |
| 18 | + |
| 19 | +## Syntax |
| 20 | + |
| 21 | +```pseudo |
| 22 | +matplotlib.pyplot.step(x, y, *args, where='pre', **kwargs) |
| 23 | +``` |
| 24 | + |
| 25 | +**Parameters:** |
| 26 | + |
| 27 | +- `x` (array-like): 1-D sequence of x positions. It is assumed (but not enforced) that `x` is increasing. |
| 28 | +- `y` (array-like): Sequence of y-values. Must have the same length as `x`. |
| 29 | +- `*args`: positional arguments forwarded to `plot()` (for example a format string such as `'o-'`). |
| 30 | +- `where` ({ `'pre'`, `'post'`, `'mid'` }, optional) — controls the placement of the steps: |
| 31 | + - `'pre'` (default): the y value is constant to the left of each x position; the interval `(x[i-1], x[i]]` has value `y[i]`. |
| 32 | + - `'post'`: the y value is constant to the right of each x position; the interval `[x[i], x[i+1])` has value `y[i]`. |
| 33 | + - `'mid'`: each step is centered between neighbors; level changes occur at midpoints between successive x values. |
| 34 | +- `**kwargs`: any other keyword arguments accepted by `matplotlib.pyplot.plot`, such as `label`, `linewidth`, `linestyle`, `alpha`, etc. |
| 35 | + |
| 36 | +**Returns:** |
| 37 | + |
| 38 | +A list of `matplotlib.lines.Line2D` objects representing the plotted steps. |
| 39 | + |
| 40 | +> **Notes:** |
| 41 | +> |
| 42 | +> - Use `plt.stairs()` if you have explicit step edges (left/right boundaries) rather than sample positions. |
| 43 | +> - `step()` is a thin wrapper around `plot()` and supports most `plot` formatting options. |
| 44 | +
|
| 45 | +## Example |
| 46 | + |
| 47 | +The example below draws three three-step series using `where='pre'`, `where='mid'`, and `where='post'`. |
| 48 | + |
| 49 | +```py |
| 50 | +import numpy as np |
| 51 | +import matplotlib.pyplot as plt |
| 52 | + |
| 53 | +x = np.linspace(0, 5, 6) |
| 54 | +y = np.array([0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1]) |
| 55 | + |
| 56 | +plt.figure(figsize=(6, 3)) |
| 57 | +plt.step(x, y + 2, where='pre', label="pre") |
| 58 | +plt.step(x, y + 1, where='mid', label="mid") |
| 59 | +plt.step(x, y + 0, where='post', label="post") |
| 60 | + |
| 61 | +plt.ylim(-0.5, 3.5) |
| 62 | +plt.xlabel('x') |
| 63 | +plt.ylabel('y') |
| 64 | +plt.title('Example: matplotlib.pyplot.step') |
| 65 | +plt.legend() |
| 66 | +plt.grid(True) |
| 67 | + |
| 68 | +plt.show() |
| 69 | +``` |
| 70 | + |
| 71 | +The output of this code will be: |
| 72 | + |
| 73 | +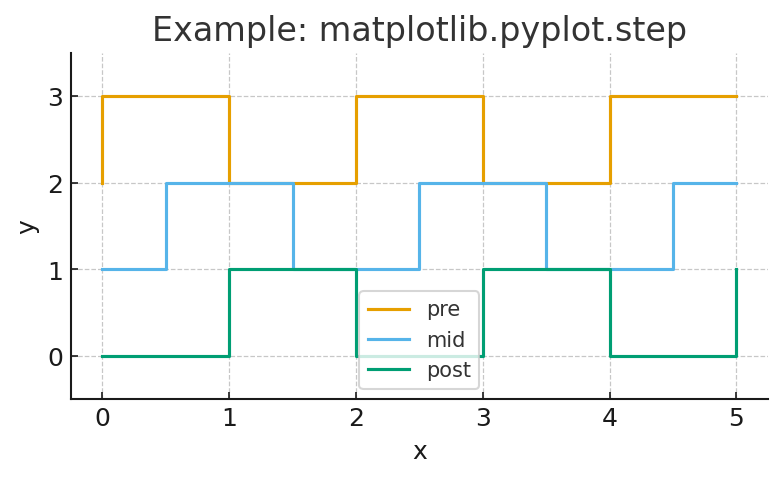 |
0 commit comments